Testing
For each dog in our breeding program, we complete the testing listed below.
GANA Standards for testing states
"Goldendoodles must be friendly, reliable, trustworthy, and well-rounded. His stability in most situations and environments, particularly with children, elderly, and the disabled, is consistent with that which is required to perform as a trained service and therapy dog.Unwarranted hostility, timidity, nervousness and/or hyperactivity should never be seen in a Goldendoodle. Dogs that exhibit any of these temperament faults should not be bred, as temperament is paramount for this breed."
Our testing is done by professional evaluators using the Volhards Puppy Aptitude Test. Only puppies that conform to the above listed traits are considered for our breeding program. Additionally, all of our puppies receive this evaluation so that we can help place puppies into homes where they will succeed in proper development. Temperament testing is done as close to day 49 as possible.
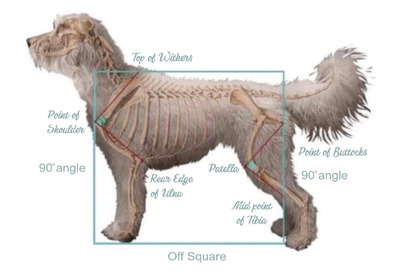
Structure
Proper structure is essential to overall health and wellbeing. Correct balance and angulation are two of the fundamental concepts used when evaluating dogs.
Balance is a term associated with the appearance and structure of a dog’s body. The term refers to the symmetrical proportion of the parts in relation to each other. It also means the relative proportion of the parts to each other. Angulation is another term associated with a dog’s body. It refers mainly to the bones of the front and rear assemblies and their angles at the hip and shoulder joints. When evaluating structure, judges look for the same angles at the shoulder and hip joints. Dogs with good balance and angulation will have a smoother stride then those who lack balance and have fewer angulations.
DNA Trait Testing
Due to genetic inheritance, each trait contains one gene from the mama and one gene from the dad.
Coat Testing
- Furnishings - Dogs with furnishings have a long mustache, long beard, and eyebrow hair. We strive for our breeding dogs to have two furnishing genes so that all offspring will be fully furnished in accordance wtih the breed standards of GANA.
- Curl - There are three different curl results possible -- curly, wavy and straight.
- Curly coats will have two curl genes.
- Wavy coats will have one curl and one straight gene.
- Straight coats will have two straight coat genes. All three coats types are recognized as proper coats.
- A fourth result is possible - a flat coat which is a dog that has two straight genes but does not have furnishings. This is considered an improper coat and is not within the breed standard.
- Shed - Dogs with furnishings tend to be low shedders regardless of their genotype for this trait.
- Color Traits - There are 12 color traits that are evaluated to determine color probability of the offspring dependant on the genes of both the mama and dad of the breeding pair.
Genetic Health Condition Testing
- Breed Relevant Testing - Genetic conditions that are known to have associated risks in goldendoodles.
- Ichthyosis, ICH1 (PNPLA1, Golden Retriever Variant)
- Von Willebrand Disease Type I, Type I vWD (VWF)
- Progressive Retinal Atrophy, prcd (PRCD Exon 1)
- Golden Retriever Progressive Retinal Atrophy 1, GR-PRA1 (SLC4A3)
- Golden Retriever Progressive Retinal Atrophy 2, GR-PRA2 (TTC8)
- Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis 5, NCL 5 (CLN5 Exon 4 Deletion, Golden Retriever Variant)
- GM2 Gangliosidosis (HEXB, Poodle Variant)
- Degenerative Myelopathy, DM (SOD1A)
- Neonatal Encephalopathy with Seizures, NEWS (ATF2)
- Identified in Standard Poodles and Small Poodles
- Muscular Dystrophy (DMD, Golden Retriever Variant)
- Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome, CMS (COLQ, Golden Retriever Variant)
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (COL7A1, Golden Retriever Variant)
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta (COL1A1, Golden Retriever Variant)
- Osteochondrodysplasia (SLC13A1, Poodle Variant)
- Intervertebral Disc Disease (Type I) (FGF4 retrogene - CFA12)
- Other Conditions not specifically related to Golden Retrievers or Poodles
Hip and Elbow X-Ray preliminary review - Canine Hip Dysplasia typically develops because of an abnormally developed hip joint, but can also be caused by cartilage damage from a traumatic fracture. Elbow dysplasia is a general term used to identify an inherited polygenic disease in the elbow.
Basic Cardiac - Each breeding dog is to be examined and classified by a veterinarian with expertise in the recognition of canine heart disease
Eye Assessment - The purpose of the OFA Companion Animal Eye Registry (CAER) is to provide breeders with information regarding canine eye diseases so that they may make informed breeding decisions in an effort to produce healthier dogs. CAER certifications will be performed by board certified (ACVO) veterinary ophthalmologists.